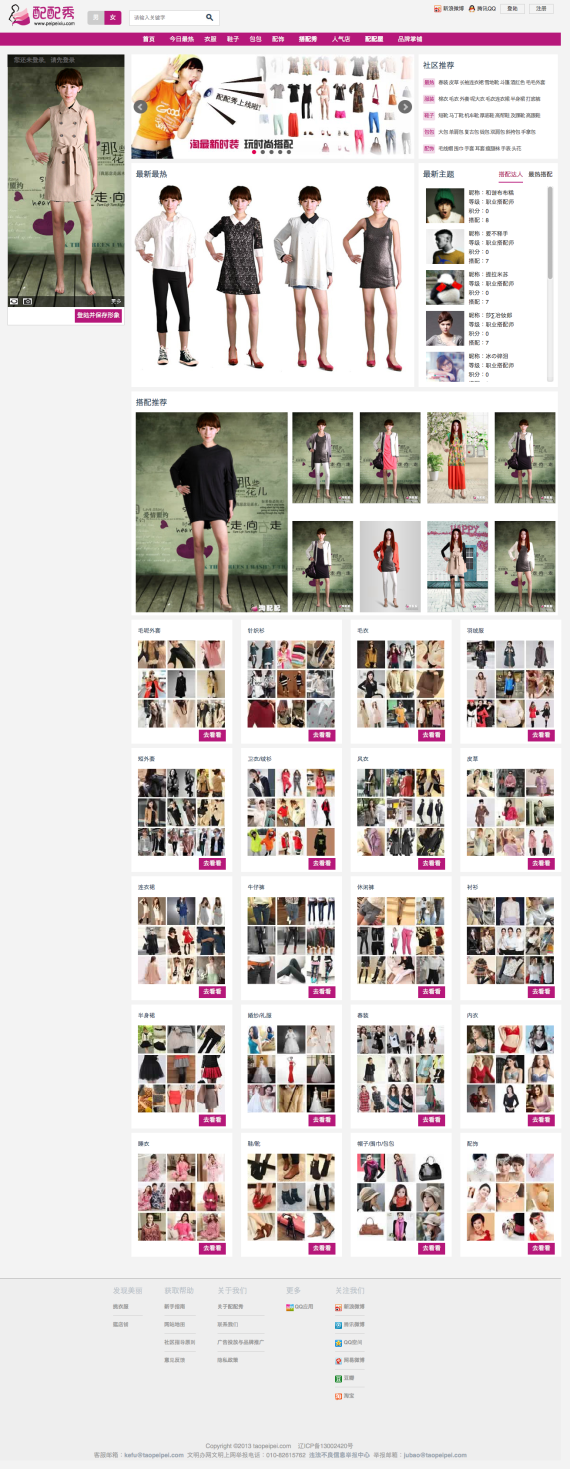
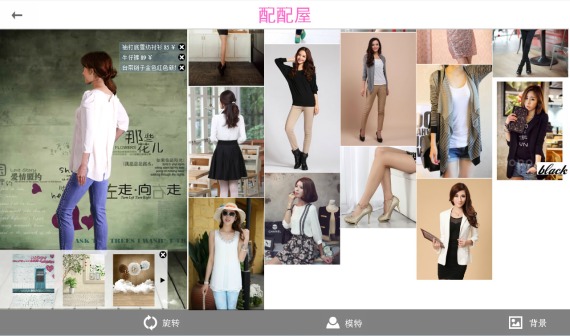
淘配配正式改名为配配秀,新版网站正式上线 http://peipeixiu.com 欢迎来搭配
10 6月
淘配配♀正式上线 一款可以搭配的逛街应用
19 2月
淘配配 试衣间效果正式提供预览(淘配配,淘宝网,衣服,鞋子,包包,配饰,家居,美容,搭配,达人,团购,淘宝店 taopeipei.cn/taopeipei.com)
预览地址: http://taopeipei.taobao.com/p/fitroom.htm 欢迎与我们联系订购。
7 2月
改进smarty使之能够定时自动清空缓存
smarty的缓存机制不是太完善,只会判断当前的缓存文件是否过期,如果过期就写入新的缓存,这样缓存只会越来越多,硬盘也总有hold不住的那天。那么,我们就来改进下smarty使之能够定时自动清空缓存。
1、打开Smarty.class.php在smarty这个类中添加一个变量:
/**
* @每2天 早上10点清空缓存
*/
var $clear_cache_time = ’2 10′;
2、在smarty类中添加两个方法:一个执行自动清空缓存的任务,一个判断是否需要清空
private function autoClearCache()
{
if($this->checkClearTime()){
$this->clear_all_cache(); //删除所有已过期的缓存
}
}private function checkClearTime()
{
$CacheParam = explode(” “,$this->clear_cache_time);if(!$this->clear_cache_time || count($CacheParam) !== 2)
{
return false;
}if(date(‘H’) != $CacheParam[1])
//当前的 小时 不为 设定的需要清空的 小时,返回false
{
return false;
}$cachetag = $this->compile_dir.”/autoclear.tag”;
//设定一个文件,用于记录上次自动清空的时间if (file_exists($cachetag))
{
$filetime = date(‘U’, filemtime($cachetag));
//返回文件内容上次修改的时间if(date(‘d’)-date(“d”,$filetime) == $CacheParam[0])
//如果现在距离上次文件修改时间的天数 为 设定的自动清空缓存的天数
{
return true ;
} else {
return false ;
}
}file_put_contents($cachetag,date(“Y-m-d H:i:s”));
//如果不存在autoclear.tag文件,则创建并写入当前时间return true;
}
3、在smarty本来的fetch方法的头部加上一句
$this->autoClearCache();
//也就是每次执行smarty的过程中,都进行自动清空缓存的操作
ok,这样简单的一个通过设定每几天 某个时间段内自动清空缓存的操作就完成了。当然,如果觉得功能满足不了自己的要求,那么开动自己的脑筋,敲敲最爱的键盘,开始自己的smarty自动清空缓存之路吧。
7 2月
Ajax 与 Smarty,第 1 部分: 使用 Smarty 开发 Ajax 应用
使用 PHP、Smarty 模板引擎和 jQuery 框架创建 Ajax 应用
简介: Smarty 是一个 PHP 模板引擎,它可以帮助您将 Web 应用的业务逻辑与表示层分离。Smarty 目前没有内置的 Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (Ajax) 支持,但是您可以轻松地扩展它的插件架构并将它与一些 JavaScript 框架整合,如 jQuery。本系列文章将阐述如何在 Ajax 应用中使用 Smarty,如何创建 Smarty 插件,以及如何改进您的 Web 应用的代码质量,使代码更具可读性和更容易维护。
在本系列文章的第一篇中,您将了解如何使用 Smarty 模板为 Ajax 请求生成 JSON、XML 和 HTML 响应。这些技术允许您在开发 PHP 代码时关注于应用逻辑,而这些应用逻辑是与 Ajax 客户端和服务器之间通信所使用的数据格式分离的。
您还将了解如何创建两个版本的表单,其中一个提供输入域让用户输入数据,另一个使用隐藏域并以不可编辑形式显示数据。通过单击一个按钮,用户能够切换两个版本的表单,使用 Ajax 向服务器提交数据并获取用于更新页面的 HTML 内容。此外,这个表单在 Web 浏览器禁用 JavaScript 时仍然能够使用。
本文的最后一部分包含配置 Smarty 和示例应用的说明。如果您的服务器或工作站启用了 SELinux,这个过程会有些复杂。这些信息对于需要修改公共文件的 Web 应用是很有用的,如内容管理系统和允许用户上传内容的网站。不管您使用的是 Smarty、流行 CMS 或定制系统,在您的代码尝试修改 Web 文件时,您都会遇到相同的与 SELinux 有关的配置问题。本文阐述了如何使用 Linux 的restorecon、chcon 和 setsebool 命令解决这些问题。
在本节中,我们将了解如何创建用来为 Ajax 请求生成响应的 Smarty 模板。您可以使用任何一种通用格式,如 JSON、XML 或 HTML。Smarty 语法主要是面向 HTML 设计的,这使它也非常适合于 XML。然而,使用 Smarty 创建 JSON 响应会有一些困难,因为模板构建的语法使用了 { 和 },这意味着如果 JSON 使用了这两个字符,您需要对它们进行转义。然而,您会发现可以修改 Smarty 的分隔符以避免这个语法冲突。您还将了解如何创建自定义修饰符和函数,并将它们注册到 Smarty 框架,这样您就能够在您的模板中使用它们了。
让我们从一个简单的例子(如清单 1 所示)开始,它将生成一个可以被 Ajax 客户端使用的 XML 响应。首先,PHP 代码应该设置内容类型以及 no-cache 响应头,它可以保证 Web 浏览器不会缓存 Ajax 响应。考虑到您以前可能没有使用过 Smarty,我们在这里简要介绍一下 demo_xml.php 文件的作用:它通过 require 包含了 Smarty 类,创建了这个类的一个实例,设置了它的编译和调试标记,使用 assign() 创建两个名为 root_attr 和 elem_data 的变量,然后使用 display() 调用一个 Smarty 模板,这样就将生成了 XML 响应。
清单 1. demo_xml.php 示例
<?php
header("Content-Type: text/xml");
header("Cache-Control: no-cache");
header("Pragma: no-cache");
require 'libs/Smarty.class.php';
$smarty = new Smarty;
$smarty->compile_check = true;
$smarty->debugging = false;
$smarty->force_compile = 1;
$smarty->assign("root_attr", "< abc & def >");
$smarty->assign('elem_data', array("111", "222", "333"));
$smarty->display('demo_xml.tpl');
?>
|
demo_xml.tpl 模板(见清单 2)生成了一个 <root> 元素,它有一个属性,它的值是从 demo_xml.php 文件的变量 root_attr 查询的。字符 <、>、"、' 和 & 分别使用 Smarty 的 escape 修饰词替换成 <、>、"、' 和 &。在 root 元素中,模板使用 Smarty 的 {section} 遍历 elem_data 数组的元素,这个数组是 demo_xml.php 文件中定义的第二个变量。demo_xml.tpl 会为数组中的每一个元素生成包含从数组查询到的值的 XML 元素。
清单 2. demo_xml.tpl 模板
<root attr="{$root_attr|escape}">
{section name="d" loop=$elem_data}
<elem>{$elem_data[d]|escape}</elem>
{/section}
</root>
|
清单 3 包含了由 demo_xml.php 文件和 demo_xml.tpl 模板生成的 XML 输出。
清单 3. XML 输出
<root attr="< abc & def >">
<elem>111</elem>
<elem>222</elem>
<elem>333</elem>
</root>
|
demo_json.php 文件(如清单 4 所示)设计了 no-cache 头,并且如清单 3 所示例子一样创建和配置了 Smarty 对象。此外,它还定义了两个名为 json_modifier() 和 json_function() 的函数,它们会调用 json_encode() PHP 函数。这两个函数被注册到 Smarty 上,这样它们就可以在模板中使用了,您将在本节的后面看到如何使用。在这之后,demo_json.php 文件创建了一些以下类型的 Smarty 变量:字符串型、数字型、布尔型和数组。然后,PHP 例子执行 demo_json.tpl 模板生成 JSON 响应。
清单 4. demo_json.php 示例
<?php
header("Content-Type: application/json");
header("Cache-Control: no-cache");
header("Pragma: no-cache");
require 'libs/Smarty.class.php';
$smarty = new Smarty;
$smarty->compile_check = true;
$smarty->debugging = false;
$smarty->force_compile = 1;
function json_modifier($value) {
return json_encode($value);
}
function json_function($params, &$smarty) {
return json_encode($params);
}
$smarty->register_modifier('json', 'json_modifier');
$smarty->register_function('json', 'json_function');
$smarty->assign('str', "a\"b\"c");
$smarty->assign('num', 123);
$smarty->assign('bool', false);
$smarty->assign('arr', array(1,2,3));
$smarty->display('demo_json.tpl');
?>
|
除了注册插件(如修饰符或函数)到 Smarty,您也可以使用 Smarty 文档中描述的一些特别的命名规范 (见 参考资料)。然后您可以将您的代码放到 plug-ins 目录,这样您的 Smarty 修饰符和函数就可以在应用的任何 Web 页面中使用。
因为 JSON 和 Smarty 的语法中都使用了 { 和 },所以您必须在 Smarty 模板中使用 {ldelim} 和 {rdelim} 生成 JSON 响应中使用的 {和 } 字符。您也可以将 { 和 } 放到 {literal} 和 {/literal} 之间。您将在另一个例子中看到,我们可以修改 Smarty 分隔符以避免这样的麻烦。
demo_json.tpl 模板(见清单 5)使用 json 修饰符对 demo_json.php 文件中的四个变量值进行编码。例如,对引号和其它特殊字符进行转义是很有用的,如字符串中的制表符和换行符。Smarty 将会在 demo_json.php 文件中模板每次使用 |json 时调用json_modifier()。json 修饰符前面必须加上 @ 字符,这样数组变量就可以传递到 json_modifier()。如果没有使用 @ 字符,修饰符函数会对数组的每一个元素进行调用。
从 demo_json.tpl 模板构建的 {json ... } 会被转换成 demo_json.php 文件的 json_function() 的一个调用。这个函数会从模板中获取一个名为 params 的数组属性,同时被传递到 json_encode(),这个函数会返回 JSON 表示的 PHP 数组。
清单 5. demo_json.tpl 模板
{ldelim}
s: {$str|json},
n: {$num|json},
b: {$bool|json},
a: {$arr|@json},
o: {json os=$str on=$num ob=$bool oa=$arr},
z: {literal}{ x: 1, y: 2 }{/literal}
{rdelim}
|
清单 6 包含了由 demo_json.php 文件和 demo_json.tpl 模板生成的 JSON 输出。
清单 6. JSON 输出
{
s: "a\"b\"c",
n: 123,
b: false,
a: [1,2,3],
o: {"os":"a\"b\"c","on":123,"ob":false,"oa":[1,2,3]},
z: { x: 1, y: 2 }
}
|
要避免在 Smarty 模板中使用 {ldelim} 和 {rdelim},您可以修改如清单 7 所示的 Smarty 分隔符。
清单 7. 修改 Smarty 分隔符
$smarty->left_delimiter = '<%'; $smarty->right_delimiter = '%>'; |
清单 8 所示的模板使用 Smarty 构件中的 <% 和 %> 分隔符生成 JSON 响应。
清单 8. demo_json2.tpl 模板
{
s: <% $str|json %>,
n: <% $num|json %>,
b: <% $bool|json %>,
a: <% $arr|@json %>,
o: <% json os=$str on=$num ob=$bool oa=$arr %>,
z: { x: 1, y: 2 }
}
|
本节的例子说明了如何使用 Smarty 生成使用 Ajax 获得的 HTML 内容。此外,这个 Web 页面也包含了一个 HTML 表单,这个表单的数据是使用 jQuery 框架以 Ajax 方式提交到服务器上的。如果 Web 浏览器禁用了 JavaScript,这个表单仍然会正确工作,Smarty 也仍然可用在服务器端生成内容。
demo_form.tpl 模板(见清单 9)包含了一个 HTML 表单,这个表单的域可能是可编辑的,也可能是不可编辑的,这取决于名为edit_mode 的变量值。这个变量是在调用模板的 PHP 代码中设置的,您将会在本节的后面看到。edit_mode 的值也会被存储在表单的一个隐藏域中。
清单 9. demo_form.tpl 模板的 HTML 表单
<form method="POST" name="demo_form">
<input type="hidden" name="edit_mode"
value="{if $edit_mode}true{else}false{/if}">
<table border="0" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0">
...
</table>
</form>
|
清单 10 显示的是表单的第一个域,如果 edit_mode 是 true,它就是一个输入框;如果 edit_mode 是 false,它就是一个隐藏域。在后一种情况中,这个域的不可编辑值会被 {$smarty.post.demo_text|escape} 包含在输出中。当用户提交这个可编辑表单时,参数demo_text 包含了用户的输入。当表单是不可编辑的,由于有一个隐藏域,这个参数仍然会出现。因此,不管表单是否可以编辑,我们都可以使用 $smarty.post.demo_text 获得这个 post 参数的值。
清单 10. demo_form.tpl 模板的文本框
<tr>
<td>Demo Text:</td>
<td>
{if $edit_mode}
<input type="text" name="demo_text" size="20"
value="{$smarty.post.demo_text|escape}">
{else}
<input type="hidden" name="demo_text"
value="{$smarty.post.demo_text|escape}">
{$smarty.post.demo_text|escape}
{/if}
</td>
</tr>
|
这个表单的下一个输入域是一个复选框(见清单 11)。在可编辑的表单中,元素 input 只有在出现参数 demo_checkbox 时才会有一个属性 checked。类似地,不可编辑的表单只有在所提交表单数据中包含了名为 demo_checkbox 的 post 参数时才会包含这个隐藏表单元素。
清单 11. demo_form.tpl 模板的复选框
<tr>
<td>Demo Checkbox:</td>
<td>
{if $edit_mode}
<input type="checkbox" name="demo_checkbox"
{if $smarty.post.demo_checkbox}checked{/if}>
{else}
{if $smarty.post.demo_checkbox}
<input type="hidden" name="demo_checkbox" value="On">
{/if}
{if $smarty.post.demo_checkbox}On{else}Off{/if}
{/if}
</td>
</tr>
|
表单的表格的下面一行包含了三个单选按钮(见清单 12)。模板代码通过比较参数 demo_radio 与每个按钮的值决定应该选择哪个单选按钮。不可编辑的表单使用一个隐藏输入域存储参数值并使用 $smarty.post.demo_radio 向用户显示这个值。
清单 12. demo_form.tpl 模板的单选按钮
<tr>
<td>Demo Radio:</td>
<td>
{if $edit_mode}
<input type="radio" name="demo_radio" value="1"
{if $smarty.post.demo_radio == '1'}checked{/if}>1
<input type="radio" name="demo_radio" value="2"
{if $smarty.post.demo_radio == '2'}checked{/if}>2
<input type="radio" name="demo_radio" value="3"
{if $smarty.post.demo_radio == '3'}checked{/if}>3
{else}
<input type="hidden" name="demo_radio"
value="{$smarty.post.demo_radio|escape}">
{$smarty.post.demo_radio|escape}
{/if}
</td>
</tr>
|
一个表单列表的选项是在一个循环的 {section} 中生成的,如清单 13 所示。当前循环的次数会被赋值给一个名为 demo_counter 的模板变量,它会与选项元素的值进行比较以便确定这个选项是否被选中。
清单 13. demo_form.tpl 模板的列表
<tr>
<td>Demo Select:</td>
<td>
{if $edit_mode}
<select name="demo_select" size="1">
{section name="demo_section" start=10 loop=100 step="10"}
{assign var="demo_counter"
value=$smarty.section.demo_section.index}
<option {if $smarty.post.demo_select == $demo_counter}
selected{/if} value="{$demo_counter}">
{$demo_counter}
</option>
{/section}
</select>
{else}
<input type="hidden" name="demo_select"
value="{$smarty.post.demo_select|escape}">
{$smarty.post.demo_select|escape}
{/if}
</td>
</tr>
|
提交按钮会根据 edit_mode 标记(见清单 14)的不同值显示不同的标签(Save 或 Edit)。onclick 属性包含了一个名为submitDemoForm() 的 JavaScript 函数调用。您将会在本文后面的内容中看到这一点,这个函数使用 Ajax 将表单数据提交到服务器,然后返回 false,这样 Web 浏览器不会多次响应按钮的单击事件而提交相同的数据。然而,如果 JavaScript 被禁用了,submitDemoForm() 将不会被调用,而 Web 浏览器就会将表单提交到服务器上。因此,这个表单不管 JavaScript 是否启用都会生效。
清单 14. demo_form.tpl 模板的提交按钮
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td>
<button type="submit" onclick="return submitDemoForm()">
{if $edit_mode}Save{else}Edit{/if}
</button>
</td>
</tr>
|
demo_page.tpl 文件(见清单 15)包含了两个 <script> 元素,其中一个是引用 jQuery,另一个是引用示例应用中的 JavaScript 文件。这个页面模板使用 Smarty 的 {include} 包含了元素 <div> 中的一个表单模板。
清单 15. demo_page.tpl 模板
<html>
<head>
<title>Demo</title>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.4.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="demo_js.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo_div">
{include file="demo_form.tpl"}
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
demo_html.php 文件(如清单 16 所示)是 Ajax 和 Smarty 之间的桥梁,负责处理 Ajax 请求并在 demo_form.tpl 模板中使用 Smarty 生成 Ajax 响应,而这个模板只有当出现一个 Ajax 请求头时才会被调用。这个头是在 JavaScript 代码中设置的,您将在下面的小节中看到。如果没有 Ajax 头,这些代码就会使用 demo_page.tpl 模板,这意味着这是 Web 浏览器 的初始页面请求或 JavaScript 被禁用。在每一个请求中,edit_mode 标记的值都会转换成另一个可编辑表单,并且它是不可编辑的。
清单 16. demo_html.php 示例
<?php
header("Cache-Control: no-cache");
header("Pragma: no-cache");
require 'libs/Smarty.class.php';
$smarty = new Smarty;
$smarty->compile_check = true;
$smarty->debugging = false;
$smarty->force_compile = 1;
$edit_mode = @($_REQUEST['edit_mode'] == "true");
$smarty->assign("edit_mode", !$edit_mode);
$ajax_request = @($_SERVER["HTTP_AJAX_REQUEST"] == "true");
$smarty->display($ajax_request ? 'demo_form.tpl' : 'demo_page.tpl');
?>
|
单击表单按钮时会调用 submitDemoForm() 函数(见清单 17)。这个函数会通过 jQuery 使用 POST 和 Web 表单的相同 URL 将表单数据发送到服务器。然后表单数据会被 jQuery 的 serialize() API 编码成一个字符串。在本例中,jQuery 在发送 Ajax 请求之前会调用beforeSend() 函数设置 Ajax-Request 头,这个信息是服务器端用以确定 Ajax 请求的。在 Ajax 请求结束后,success() 函数会被调用。这个回调函数会将响应内容插入到 Web 页面的 <div> 元素中。
清单 17. demo_js.js 示例
function submitDemoForm() {
var form = $("form[name=demo_form]");
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: form.action ? form.action : document.URL,
data: $(form).serialize(),
dataType: "text",
beforeSend: function(xhr) {
xhr.setRequestHeader("Ajax-Request", "true");
},
success: function(response) {
$("#demo_div").html(response);
}
});
return false;
}
|
在解压缩示例应用后,您应该会看一个名为 ajaxsmarty 的目录,它包含了多个 PHP 文件、一个 JavaScript 文件和四个子目录:cache、configs、templates 和 templates_c。模板目录包含了示例应用的 Smarty 模板。其它三个子目录是空的。
下载最新稳定版本的 Smarty (见 参考资料),然后解压缩它。(示例项目是在 Smarty 2.6.25 下测试的。)接下来,将 Smarty 的子目录 libs 复制到 ajaxsmarty 目录,这个目录是示例应用的主目录。
将 ajaxsmarty 目录(同时包含示例应用和 Smarty 的 libs)上传或复制到 Apache 的 HTML 目录。如果您使用的是一个 Web 主机公司的服务器,SELinux 可能被禁用了,因为启用 SELinux 可能会有太多的支持呼叫。如果你在自己的 Linux 服务器上测试应用,您的服务器有可能启用了 SELinux,那么当浏览器请求一个 PHP 文件时您可能会得到下面的错误:“SELinux is preventing the httpd from using potentially mislabeled files.” 解决方法是以 root 身份运行清单 18 所示的命令。
清单 18. 设置 Web 文件的安全性上下文(标签)
restorecon -R -v /var/www/html/ajaxsmarty |
至此,您应该能够在浏览器上打开地址:http://localhost/ajaxsmarty/,页面会显示三个链接。如果您单击其中一个链接,您会在 Web 浏览器上得到以下的 Smarty 错误:“Fatal error: Smarty error: unable to write to $compile_dir ‘/var/www/html/ajaxsmarty/templates_c’. Be sure $compile_dir is writable by the Web server user. in /var/www/html/ajaxsmarty/libs/Smarty.class.php on line 1113”。
出现上面的错误是因为 Smarty 安装还没有完成。您必须给 Web 服务器写 templates_c 和 cache 目录的用户权限。实现这一步的正确做法是修改它们的拥有者,如清单 19 所示。注意 apache 用户名和服务器的 HTML 目录在您的计算机上可能会有所不同。
清单 19. 修改两个目录的拥有者使 Smarty 能够创建文件
chown apache:apache /var/www/html/ajaxsmarty/templates_c chown apache:apache /var/www/html/ajaxsmarty/cache |
如果您不是使用 root 用户登录,您是不能使用 chown 修改 templates_c 和 cache 的写权限的。您可以通过使用 FTP 客户端修改,或者使用 chmod 命令将权限设置为 777。允许所有用户都能写这些文件夹不是一个非常好的做法,但是如果您不能使用 chown 命令,这是您唯一快速有效的方法。如果您的 Web 服务器是公共的,您应该联系服务器管理员帮您完成这个修改。
如果您的计算机启用了 SELinux,您可能还会在浏览器上遇到这样的一个错误:“SELinux prevented httpd reading and writing access to http files.” 或 “SELinux is preventing httpd (httpd_t) write to ./templates_c (public_content_rw_t).” 解决方法是以 root 身份运行清单 20 中的命令。
清单 20. 在启用 SELinux 时允许 Smarty 在它的目录中创建文件
chcon -t public_content_rw_t /var/www/html/ajaxsmarty/templates_c chcon -t public_content_rw_t /var/www/html/ajaxsmarty/cache setsebool -P allow_httpd_anon_write=1 |
带有 allow_httpd_anon_write 参数的 setsebool 命令必须只执行一次。它允许 httpd 守护进程将文件写到 public_content_rw_t 目录中。
在本文中,您了解了如何创建为 Ajax 请求产生 JSON、XML 和 HTML 响应的 Smarty 模板,如何使用 Smarty 创建一个即使在 Web 浏览器禁用 JavaScript 时仍然有效的 Ajax 表单,以及如何在启用 SELinux 的 Linux 主机上配置 Smarty。
下载
| 描述 | 名字 | 大小 | 下载方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 本文样例应用 | ajaxsmarty_part1_src.zip | 5KB | HTTP |
关于下载方法的信息
参考资料
学习
- Smarty 手册 包含了所有需要了解的 Smarty 信息。
- 查看这个基于 Smarty 的 示例应用。
- “用 Smarty 分离 PHP 应用程序中的形式与功能”(developerWorks,2007 年 7 月)是 developerWorks 提供的一个 Smarty 介绍文章。
- jQuery 框架是 Smarty 的补充,它添加了所需要的 JavaScript 功能,如 Ajax。
- developerWorks Web development 专区:通过专门关于 Web 技术的文章和教程,扩展您在网站开发方面的技能。
- developerWorks Ajax 资源中心:这是有关 Ajax 编程模型信息的一站式中心,包括很多文档、教程、论坛、blog、wiki 和新闻。任何 Ajax 的新信息都能在这里找到。
- developerWorks Web 2.0 资源中心,这是有关 Web 2.0 相关信息的一站式中心,包括大量 Web 2.0 技术文章、教程、下载和相关技术资源。您还可以通过 Web 2.0 新手入门 栏目,迅速了解 Web 2.0 的相关概念。
获得产品和技术
- 下载 Smarty 并使用它。
讨论
- 访问 Smarty 官方 论坛。
- My developerWorks 中文社区
Andrei Cioroianu 是 Devsphere 公司的创始人,该公司专门提供 Java EE 开发和 Web 2.0/Ajax 顾问服务。他自 1997 年就开始使用 Java 和 Web 技术,具有 10 多年解决复杂技术问题和管理商业产品的整个生命周期以及定制应用程序和开源框架的专业经验。您可以通过 www.devsphere.com 上的联系列表与 Andrei 联系。
1 11月
Stage3D developer tips

Stage3D developer tips:
- Flash Sockets Example in Unity3D
- Context3D.setRenderToTexture and Context3D.setRenderToBackBuffer
- New Mouse Events for Away3D 4.0
- Procedurally-Generated Cylinder
- Citrus Engine on Nape and physics performance improvement
- Stage3D Picking: Mouse and Touch Interaction
- Stateless particle system on GPU
- I don’t need flash.geom.Matrix3D class anymore
- Compress 3D model next
- Procedurally-Generated Sphere
- Getting Stage3D To Work On IPhone, With AIR 3.2 And Flashdevelop
- Sprite Buddy
- StarlingMXMLSpriteSheet
- Alternativa3D: Drawing on material
- Export .obj from Alternativa3D
- Alternativa3D: Dragging a 3D object
- Click in the Starling Framework
- Double the Performance of Stage3D Apps
- Performance: Starling vs GPU Render Mode
- Drawing MadComponents with Stage3D
- Genome2D on top of Away3D
- Starling Framework Extension (Games)
- How to Detect Software Render Mode with Flare3D
- Genome2D rendering the display list
- Faster Stage3D Rendering With View Frustum Culling
- Starling UML Class Diagram
- Spritesheets With Minko
- Starling Texture test on the Nook color
- Genome2D GShape component
- Assets Loading & Management in Away3D
- [Flash] -swf-version meaning
- Radial blur in AGAL
- Tricks when starting using the Starling framework
- UV Scrolling in Starling
- FastStats (DisplayList, ND2D, Starling)
- AS3 Box2D debug mode in Starling
- Flash Builder 4.6 + Away3D + AIR 3.2 + iOS
- Making Scrollable Tiles with UV Offsets in Stage3D and AGAL
- Backstage2D – the GPU Augmented Flash Display List
- LG SmartTVs, Adobe AIR 3.0 and App Test
- Adobe AIR 3.0 on TV (developer toolchain)
- ShiVa Flash: ActionScript 3 Interaction
- Minko 2 Developers Reference
- Camera orbit controller Flare3D 2.0
- DDS2ATF – Tool for converting DDS files into ATF files suitable for use with the Flash Stage3D API
- Pure AS3 librairies for encode/decode ATF (Adobe Texture Format) files
- Using Starling and haxe
- GLSL -> AGAL compiler
- Stage3D KIL Command
- Stepping Through The Stage3D Pipeline
- Frustum Culling – on steroids!
- Creating Tilemaps from Bitmaps with Axel
- Stage3D compressed textures – Introducing the ATF SDK
- Stage3D Post-Processing Special Effects
- Using Object Pooling in the design of a Particle System
- Choosing frame rate
- Detecting Pepper based Flash Player
- Playing with Feathers UI Components for Starling Framework
- Utilizing Multiple Worker in AS3
- Extendable AS3 Worker Class
- From vector to raster
- UPDATED: [Flash] -swf-version meaning
- Analytics in Unity Flash
- Use Any Sprite As a Stage3D Texture
- AGAL cheat-sheet illustration
Flash Player 11 & Stage3D round-up:
- AS3 Concurrency/Workers use cases, best practices, and link roundup
- Choosing frame rate (UPDATED)
- Blog about FLASC
- Combined version of the Flex 4.6 and AIR 3.5 SDK for the lazy ones
- Batching utility for ATF textures
- Compressed Stage3D Textures With ATF
- AS3 Workers: Concurrent Fluid Dynamics and Box2D Physics with ActionScript Workers
- AS3 Workers: More Experiments with Concurrent Fluid Dynamics & Box2D Physics
- Compression Speed Followup
- Tools to compliment Flash’s Telemetry feature
- AS3 Quickie – Frame Label Events
7 3月
CSS 妙用(The Skinny on CSS Attribute Selectors)
by: Chris Coyier
CSS has the ability to target HTML elements based on any one of their attributes. You probably already know about classes and IDs. Check out this bit of HTML:
<h2 id="title" class="magic" rel="friend">David Walsh</h2>This single element has three attributes: ID, class, and rel. To select the element in CSS, you could use and ID selector (#first-title) or a class selector (.magical). But did you know you can select it based on that rel attribute as well? That is what is known as an attribute selector:
h2[rel="friend"] { /* woohoo! */ }There is a lot more to attribute selectors though, so let’s look closer at all the different options and try to cover some “real world” scenarios on when they might be useful.
Attribute Exactly Equals Certain Value
In the example we used above, the attribute of the h2 element was “friend”. The CSS selector we wrote targeted that h2 element because it’s rel attribute was exactly “friend”. In other words, that equals sign means just just what you think it does… an exact match. See another basic example:
<h1 rel="external">Attribute Equals</h1>h1[rel="external"] { color: red; }
A great real world example of this is styling a blogroll. Let’s say you had a list of links to friends sites like this:
<a href="http://perishablepress.com">Jeff Starr</a> <a href="http://davidwalsh.name">David Walsh</a> <a href="http://accidentalninja.net/">Richard Felix</a>Then you wanted to style each link slightly differently. The traditional way would probably be to give each link a class name in which to target, but that requires additional markup which is always a nice thing to avoid (semantics and all). Another way might be to use :nth-child, but that requires their order to never change. This is the perfect use for attribute selectors… the links already have a unique attribute in which to target!
a[href="http://perishablepress.com"] { color: red; }I believe the most common use of regular attribute selectors is on inputs. There are text, button, checkbox, file, hidden, image, password, radio, reset, and submit (did I miss any?). All of them are <input>’s, and all of them are very different. So doing something like input { padding: 10px; } is a bad idea most of the time. It’s very common to see things like:
input[type="text"] { padding: 3px; } input[type="radio"] { float: left; }It’s really the only way to get your hands on certain types of inputs without screwing up the others and without adding extra markup.
Note on Quotes: You can usually get away without using quotes in attribute selectors, like [type=radio], but the rules for omitting quotes are weird and inconsistent across actual browser implementations. So, best practice, just use quotes, like [type=”radio”]. It’s safer and always works.
Attribute Contains Certain Value Somewhere
This is where it starts getting more interesting. The equals sign in attribute selectors may be prefaced by other characters which alter the meaning a bit. For example, “*=” means “match the following value anywhere in the attribute value.” Look at this example:
<h1 rel="xxxexternalxxx">Attribute Contains</h1>h1[rel*="external"] { color: red; }
Remember that classes and ID’s are attributes too, and can be used used with attribute selectors. So let’s say you were writing CSS for a site where you couldn’t control the markup and a sloppy developer had three DIVs you need to target:
<div id="post_1"></div> <div id="post_two"></div> <div id="third_post"></div>You could select them all with:
div[id*="post"] { color: red; }Attribute Begins with Certain Value
<h1 rel="external-link yep">Attribute Begins</h1>h1[rel^="external"] { color: red; }
A real world example of using this would be, say, that you wanted to style every single link to your friends site different than other links. Doesn’t matter if you are linking to their homepage or any subpage, any links to them you want to style up.
a[href^="http://perishablepress.com"] { color: red; }That will match a link to their homepage, but also any other subpages as well.
Attribute Ends with Certain Value
We can select based on how attribute values begin, why not end?
<h1 rel="friend external">Attribute Ends</h1>h1[rel$="external"] { color: red; }
Honestly I struggle a bit to find the perfect real world example of using this, but I do like that it exists. Perhaps you could use it to look for links that end in characters that will likely have no significant effect:
a[href$="#"], a[href$=?] { color: red; }Attribute is within Space Separated List
You probably already knew that you could apply multiple classes to elements right? Well if you do that, you can still use .class-name in CSS to target any one of them. Attribute selectors aren’t that easy. If your rel attribute has multiple values (e.g. values in a space separated list) you’ll need to use “~=”:
<h1 rel="friend external sandwich">Attribute Space Separated</h1>h1[rel~="external"] { color: red; }
You might be thinking, why would I use this when *= would also match this and be more versatile? Indeed it is more versatile, but it can be too versatile. This selector requires the spaces around the value where as *= would not. So if you had two elements one with rel=home friend-link and one with rel=home friend link you are going to need the space-separated selector to target the second one properly.
Attribute is the start of a Dash Separated List
This will select if the start of a dash-separated list of attribute values matches the selector. Not particularly useful, since [attr^=value] also does that.
<h1 rel="friend-external-sandwich">Attribute Dash Separated</h1>h1[rel|="friend"] { color: red; }
Multiple Attribute Matches
Vital to note is that you can use multiple attribute selectors in the same selector, which requires all of them to match for the selector itself to match.
<h1 rel="handsome" title="Important note">Multiple Attributes</h1>h1[rel="handsome"][title^="Important"] { color: red; }
Browser Support
Every single example above works in all modern browsers: Safari, Chrome, Firefox, Opera, and IE. Internet Explorer has perfect support for all of these down to version 7, but zero support in 6. To test in your browser, see the test page. If the line/selector style is in red, it works.
28 2月
SQL语法大全
一、基础
1、说明:创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE database-name
2、说明:删除数据库
drop database dbname
3、说明:备份sql server
— 创建 备份数据的 device
USE master
EXEC sp_addumpdevice ‘disk’, ‘testBack’, ‘c:\mssql7backup\MyNwind_1.dat’
— 开始 备份
BACKUP DATABASE pubs TO testBack
4、说明:创建新表
create table tabname(col1 type1 [not null] [primary key],col2 type2 [not null],..)
根据已有的表创建新表:
A:create table tab_new like tab_old (使用旧表创建新表)
B:create table tab_new as select col1,col2… from tab_old definition only
5、说明:删除新表
drop table tabname
6、说明:增加一个列
Alter table tabname add column col type
注:列增加后将不能删除。DB2中列加上后数据类型也不能改变,唯一能改变的是增加varchar类型的长度。
7、说明:添加主键: Alter table tabname add primary key(col)
说明:删除主键: Alter table tabname drop primary key(col)
8、说明:创建索引:create [unique] index idxname on tabname(col….)
删除索引:drop index idxname
注:索引是不可更改的,想更改必须删除重新建。
9、说明:创建视图:create view viewname as select statement
删除视图:drop view viewname
10、说明:几个简单的基本的sql语句
选择:select * from table1 where 范围
插入:insert into table1(field1,field2) values(value1,value2)
删除:delete from table1 where 范围
更新:update table1 set field1=value1 where 范围
查找:select * from table1 where field1 like ’%value1%’ —like的语法很精妙,查资料!
排序:select * from table1 order by field1,field2 [desc]
总数:select count as totalcount from table1
求和:select sum(field1) as sumvalue from table1
平均:select avg(field1) as avgvalue from table1
最大:select max(field1) as maxvalue from table1
最小:select min(field1) as minvalue from table1
11、说明:几个高级查询运算词
A: UNION 运算符
UNION 运算符通过组合其他两个结果表(例如 TABLE1 和 TABLE2)并消去表中任何重复行而派生出一个结果表。当 ALL 随 UNION 一起使用时(即 UNION ALL),不消除重复行。两种情况下,派生表的每一行不是来自 TABLE1 就是来自 TABLE2。
B: EXCEPT 运算符
EXCEPT 运算符通过包括所有在 TABLE1 中但不在 TABLE2 中的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果表。当 ALL 随 EXCEPT 一起使用时 (EXCEPT ALL),不消除重复行。
C: INTERSECT 运算符
INTERSECT 运算符通过只包括 TABLE1 和 TABLE2 中都有的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果表。当 ALL 随 INTERSECT 一起使用时 (INTERSECT ALL),不消除重复行。
注:使用运算词的几个查询结果行必须是一致的。
12、说明:使用外连接
A、left (outer) join:
左外连接(左连接):结果集几包括连接表的匹配行,也包括左连接表的所有行。
SQL: select a.a, a.b, a.c, b.c, b.d, b.f from a LEFT OUT JOIN b ON a.a = b.c
B:right (outer) join:
右外连接(右连接):结果集既包括连接表的匹配连接行,也包括右连接表的所有行。
C:full/cross (outer) join:
全外连接:不仅包括符号连接表的匹配行,还包括两个连接表中的所有记录。
12、分组:Group by:
一张表,一旦分组 完成后,查询后只能得到组相关的信息。
组相关的信息:(统计信息) count,sum,max,min,avg 分组的标准)
在SQLServer中分组时:不能以text,ntext,image类型的字段作为分组依据
在selecte统计函数中的字段,不能和普通的字段放在一起;
13、对数据库进行操作:
分离数据库: sp_detach_db; 附加数据库:sp_attach_db 后接表明,附加需要完整的路径名
14.如何修改数据库的名称:
sp_renamedb ‘old_name’, ‘new_name’
二、提升
1、说明:复制表(只复制结构,源表名:a 新表名:b) (Access可用)
法一:select * into b from a where 11(仅用于SQlServer)
法二:select top 0 * into b from a
2、说明:拷贝表(拷贝数据,源表名:a 目标表名:b) (Access可用)
insert into b(a, b, c) select d,e,f from b;
3、说明:跨数据库之间表的拷贝(具体数据使用绝对路径) (Access可用)
insert into b(a, b, c) select d,e,f from b in ‘具体数据库’ where 条件
例子:..from b in ‘”&Server.MapPath(“.”)&”\data.mdb” &”‘ where..
4、说明:子查询(表名1:a 表名2:b)
select a,b,c from a where a IN (select d from b ) 或者: select a,b,c from a where a IN (1,2,3)
5、说明:显示文章、提交人和最后回复时间
select a.title,a.username,b.adddate from table a,(select max(adddate) adddate from table where table.title=a.title) b
6、说明:外连接查询(表名1:a 表名2:b)
select a.a, a.b, a.c, b.c, b.d, b.f from a LEFT OUT JOIN b ON a.a = b.c
7、说明:在线视图查询(表名1:a )
select * from (SELECT a,b,c FROM a) T where t.a > 1;
8、说明:between的用法,between限制查询数据范围时包括了边界值,not between不包括
select * from table1 where time between time1 and time2
select a,b,c, from table1 where a not between 数值1 and 数值2
9、说明:in 的使用方法
select * from table1 where a [not] in (‘值1’,’值2’,’值4’,’值6’)
10、说明:两张关联表,删除主表中已经在副表中没有的信息
delete from table1 where not exists ( select * from table2 where table1.field1=table2.field1 )
11、说明:四表联查问题:
select * from a left inner join b on a.a=b.b right inner join c on a.a=c.c inner join d on a.a=d.d where …..
12、说明:日程安排提前五分钟提醒
SQL: select * from 日程安排 where datediff(‘minute’,f开始时间,getdate())>5
13、说明:一条sql 语句搞定数据库分页
select top 10 b.* from (select top 20 主键字段,排序字段 from 表名 order by 排序字段 desc) a,表名 b where b.主键字段 = a.主键字段 order by a.排序字段
具体实现:
关于数据库分页:
declare @start int,@end int
@sql nvarchar(600)
set @sql=’select top’+str(@end-@start+1)+’+from T where rid not in(select top’+str(@str-1)+’Rid from T where Rid>-1)’
exec sp_executesql @sql
–注意:在top后不能直接跟一个变量,所以在实际应用中只有这样的进行特殊的处理。Rid为一个标识列,如果top后还有具—体的字段,这样做是非常有好处的。因为这样可以避免 top的字段如果是逻辑索引的,查询的结果后实际表中的不一致(逻–辑索引中的数据有可能和数据表中的不一致,而查询时如果处在索引则首先查询索引)
14、说明:前10条记录
select top 10 * form table1 where 范围
–5、说明:选择在每一组b值相同的数据中对应的a最大的记录的所有信息(类似这样的用法可以用于论坛每月排行榜,每月热销产品分析,按科目成绩排名,等等.)
select a,b,c from tablename ta where a=(select max(a) from tablename tb where tb.b=ta.b)
16、说明:包括所有在 TableA 中但不在 TableB和TableC 中的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果表
(select a from tableA ) except (select a from tableB) except (select a from tableC)
17、说明:随机取出10条数据
select top 10 * from tablename order by newid()
18、说明:随机选择记录
select newid()
19、说明:删除重复记录
1),delete from tablename where id not in (select max(id) from tablename group by col1,col2,…)
2),select distinct * into temp from tablename
delete from tablename
insert into tablename select * from temp
评价: 这种操作牵连大量的数据的移动,这种做法不适合大容量但数据操作
3),例如:在一个外部表中导入数据,由于某些原因第一次只导入了一部分,但很难判断具体位置,这样只有在下一次全部导入,这样也就产生好多重复的字段,怎样删除重复字段
alter table tablename
–添加一个自增列
add column_b int identity(1,1)
delete from tablename where column_b not in(
select max(column_b) from tablename group by column1,column2,…)
alter table tablename drop column column_b
20、说明:列出数据库里所有的表名
select name from sysobjects where type=’U’ // U代表用户
21、说明:列出表里的所有的列名
select name from syscolumns where id=object_id(‘TableName’)
22、说明:列示type、vender、pcs字段,以type字段排列,case可以方便地实现多重选择,类似select 中的case。
select type,sum(case vender when ‘A’ then pcs else 0 end),sum(case vender when ‘C’ then pcs else 0 end),sum(case vender when ‘B’ then pcs else 0 end) FROM tablename group by type
显示结果:
type vender pcs
电脑 A 1
电脑 A 1
光盘 B 2
光盘 A 2
手机 B 3
手机 C 3
23、说明:初始化表table1
TRUNCATE TABLE table1
24、说明:选择从10到15的记录
select top 5 * from (select top 15 * from table order by id asc) table_别名 order by id desc
三、技巧
1、1=1,1=2的使用,在SQL语句组合时用的较多
“where 1=1” 是表示选择全部 “where 1=2”全部不选,
如:
if @strWhere !=”
begin
set @strSQL = ‘select count(*) as Total from [‘ + @tblName + ‘] where ‘ + @strWhere
end
else
begin
set @strSQL = ‘select count(*) as Total from [‘ + @tblName + ‘]’
end
我们可以直接写成
错误!未找到目录项。
set @strSQL = ‘select count(*) as Total from [‘ + @tblName + ‘] where 1=1 安定 ‘+ @strWhere 2、收缩数据库
–重建索引
DBCC REINDEX
DBCC INDEXDEFRAG
–收缩数据和日志
DBCC SHRINKDB
DBCC SHRINKFILE
3、压缩数据库
dbcc shrinkdatabase(dbname)
4、转移数据库给新用户以已存在用户权限
exec sp_change_users_login ‘update_one’,’newname’,’oldname’
go
5、检查备份集
RESTORE VERIFYONLY from disk=’E:\dvbbs.bak’
6、修复数据库
ALTER DATABASE [dvbbs] SET SINGLE_USER
GO
DBCC CHECKDB(‘dvbbs’,repair_allow_data_loss) WITH TABLOCK
GO
ALTER DATABASE [dvbbs] SET MULTI_USER
GO
7、日志清除
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @LogicalFileName sysname,
@MaxMinutes INT,
@NewSize INT
USE tablename — 要操作的数据库名
SELECT @LogicalFileName = ‘tablename_log’, — 日志文件名
@MaxMinutes = 10, — Limit on time allowed to wrap log.
@NewSize = 1 — 你想设定的日志文件的大小(M)
Setup / initialize
DECLARE @OriginalSize int
SELECT @OriginalSize = size
FROM sysfiles
WHERE name = @LogicalFileName
SELECT ‘Original Size of ‘ + db_name() + ‘ LOG is ‘ +
CONVERT(VARCHAR(30),@OriginalSize) + ‘ 8K pages or ‘ +
CONVERT(VARCHAR(30),(@OriginalSize*8/1024)) + ‘MB’
FROM sysfiles
WHERE name = @LogicalFileName
CREATE TABLE DummyTrans
(DummyColumn char (8000) not null)
DECLARE @Counter INT,
@StartTime DATETIME,
@TruncLog VARCHAR(255)
SELECT @StartTime = GETDATE(),
@TruncLog = ‘BACKUP LOG ‘ + db_name() + ‘ WITH TRUNCATE_ONLY’
DBCC SHRINKFILE (@LogicalFileName, @NewSize)
EXEC (@TruncLog)
— Wrap the log if necessary.
WHILE @MaxMinutes > DATEDIFF (mi, @StartTime, GETDATE()) — time has not expired
AND @OriginalSize = (SELECT size FROM sysfiles WHERE name = @LogicalFileName)
AND (@OriginalSize * 8 /1024) > @NewSize
BEGIN — Outer loop.
SELECT @Counter = 0
WHILE ((@Counter < @OriginalSize / 16) AND (@Counter < 50000))
BEGIN — update
INSERT DummyTrans VALUES ('Fill Log') DELETE DummyTrans
SELECT @Counter = @Counter + 1
END
EXEC (@TruncLog)
END
SELECT 'Final Size of ' + db_name() + ' LOG is ' +
CONVERT(VARCHAR(30),size) + ' 8K pages or ' +
CONVERT(VARCHAR(30),(size*8/1024)) + 'MB'
FROM sysfiles
WHERE name = @LogicalFileName
DROP TABLE DummyTrans
SET NOCOUNT OFF
8、说明:更改某个表
exec sp_changeobjectowner 'tablename','dbo'
9、存储更改全部表
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.User_ChangeObjectOwnerBatch
@OldOwner as NVARCHAR(128),
@NewOwner as NVARCHAR(128)
AS
DECLARE @Name as NVARCHAR(128)
DECLARE @Owner as NVARCHAR(128)
DECLARE @OwnerName as NVARCHAR(128)
DECLARE curObject CURSOR FOR
select 'Name' = name,
'Owner' = user_name(uid)
from sysobjects
where user_name(uid)=@OldOwner
order by name
OPEN curObject
FETCH NEXT FROM curObject INTO @Name, @Owner
WHILE(@@FETCH_STATUS=0)
BEGIN
if @Owner=@OldOwner
begin
set @OwnerName = @OldOwner + '.' + rtrim(@Name)
exec sp_changeobjectowner @OwnerName, @NewOwner
end
— select @name,@NewOwner,@OldOwner
FETCH NEXT FROM curObject INTO @Name, @Owner
END
close curObject
deallocate curObject
GO
10、SQL SERVER中直接循环写入数据
declare @i int
set @i=1
while @i<30
begin
insert into test (userid) values(@i)
set @i=@i+1
end
案例:
有如下表,要求就裱中所有沒有及格的成績,在每次增長0.1的基礎上,使他們剛好及格:
Name score
Zhangshan 80
Lishi 59
Wangwu 50
Songquan 69
while((select min(score) from tb_table)<60)
begin
update tb_table set score =score*1.01
where score60
break
else
continue
end
数据开发-经典
1.按姓氏笔画排序:
Select * From TableName Order By CustomerName Collate Chinese_PRC_Stroke_ci_as //从少到多
2.数据库加密:
select encrypt(‘原始密码’)
select pwdencrypt(‘原始密码’)
select pwdcompare(‘原始密码’,’加密后密码’) = 1–相同;否则不相同 encrypt(‘原始密码’)
select pwdencrypt(‘原始密码’)
select pwdcompare(‘原始密码’,’加密后密码’) = 1–相同;否则不相同
3.取回表中字段:
declare @list varchar(1000),
@sql nvarchar(1000)
select @list=@list+’,’+b.name from sysobjects a,syscolumns b where a.id=b.id and a.name=’表A’
set @sql=’select ‘+right(@list,len(@list)-1)+’ from 表A’
exec (@sql)
4.查看硬盘分区:
EXEC master..xp_fixeddrives
5.比较A,B表是否相等:
if (select checksum_agg(binary_checksum(*)) from A)
=
(select checksum_agg(binary_checksum(*)) from B)
print ‘相等’
else
print ‘不相等’
6.杀掉所有的事件探察器进程:
DECLARE hcforeach CURSOR GLOBAL FOR SELECT ‘kill ‘+RTRIM(spid) FROM master.dbo.sysprocesses
WHERE program_name IN(‘SQL profiler’,N’SQL 事件探查器’)
EXEC sp_msforeach_worker ‘?’
7.记录搜索:
开头到N条记录
Select Top N * From 表
——————————-
N到M条记录(要有主索引ID)
Select Top M-N * From 表 Where ID in (Select Top M ID From 表) Order by ID Desc
———————————-
N到结尾记录
Select Top N * From 表 Order by ID Desc
案例
例如1:一张表有一万多条记录,表的第一个字段 RecID 是自增长字段, 写一个SQL语句, 找出表的第31到第40个记录。
select top 10 recid from A where recid not in(select top 30 recid from A)
分析:如果这样写会产生某些问题,如果recid在表中存在逻辑索引。
select top 10 recid from A where……是从索引中查找,而后面的select top 30 recid from A则在数据表中查找,这样由于索引中的顺序有可能和数据表中的不一致,这样就导致查询到的不是本来的欲得到的数据。
解决方案
1, 用order by select top 30 recid from A order by ricid 如果该字段不是自增长,就会出现问题
2, 在那个子查询中也加条件:select top 30 recid from A where recid>-1
例2:查询表中的最后以条记录,并不知道这个表共有多少数据,以及表结构。
set @s = ‘select top 1 * from T where pid not in (select top ‘ + str(@count-1) + ‘ pid from T)’
print @s exec sp_executesql @s
9:获取当前数据库中的所有用户表
select Name from sysobjects where xtype=’u’ and status>=0
10:获取某一个表的所有字段
select name from syscolumns where id=object_id(‘表名’)
select name from syscolumns where id in (select id from sysobjects where type = ‘u’ and name = ‘表名’)
两种方式的效果相同
11:查看与某一个表相关的视图、存储过程、函数
select a.* from sysobjects a, syscomments b where a.id = b.id and b.text like ‘%表名%’
12:查看当前数据库中所有存储过程
select name as 存储过程名称 from sysobjects where xtype=’P’
13:查询用户创建的所有数据库
select * from master..sysdatabases D where sid not in(select sid from master..syslogins where name=’sa’)
或者
select dbid, name AS DB_NAME from master..sysdatabases where sid 0x01
14:查询某一个表的字段和数据类型
select column_name,data_type from information_schema.columns
where table_name = ‘表名’
15:不同服务器数据库之间的数据操作
–创建链接服务器
exec sp_addlinkedserver ‘ITSV ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘远程服务器名或ip地址 ‘
exec sp_addlinkedsrvlogin ‘ITSV ‘, ‘false ‘,null, ‘用户名 ‘, ‘密码 ‘
–查询示例
select * from ITSV.数据库名.dbo.表名
–导入示例
select * into 表 from ITSV.数据库名.dbo.表名
–以后不再使用时删除链接服务器
exec sp_dropserver ‘ITSV ‘, ‘droplogins ‘
–连接远程/局域网数据(openrowset/openquery/opendatasource)
–1、openrowset
–查询示例
select * from openrowset( ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘sql服务器名 ‘; ‘用户名 ‘; ‘密码 ‘,数据库名.dbo.表名)
–生成本地表
select * into 表 from openrowset( ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘sql服务器名 ‘; ‘用户名 ‘; ‘密码 ‘,数据库名.dbo.表名)
–把本地表导入远程表
insert openrowset( ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘sql服务器名 ‘; ‘用户名 ‘; ‘密码 ‘,数据库名.dbo.表名)
select *from 本地表
–更新本地表
update b
set b.列A=a.列A
from openrowset( ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘sql服务器名 ‘; ‘用户名 ‘; ‘密码 ‘,数据库名.dbo.表名)as a inner join 本地表 b
on a.column1=b.column1
–openquery用法需要创建一个连接
–首先创建一个连接创建链接服务器
exec sp_addlinkedserver ‘ITSV ‘, ‘ ‘, ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘远程服务器名或ip地址 ‘
–查询
select *
FROM openquery(ITSV, ‘SELECT * FROM 数据库.dbo.表名 ‘)
–把本地表导入远程表
insert openquery(ITSV, ‘SELECT * FROM 数据库.dbo.表名 ‘)
select * from 本地表
–更新本地表
update b
set b.列B=a.列B
FROM openquery(ITSV, ‘SELECT * FROM 数据库.dbo.表名 ‘) as a
inner join 本地表 b on a.列A=b.列A
–3、opendatasource/openrowset
SELECT *
FROM opendatasource( ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘Data Source=ip/ServerName;User ID=登陆名;Password=密码 ‘ ).test.dbo.roy_ta
–把本地表导入远程表
insert opendatasource( ‘SQLOLEDB ‘, ‘Data Source=ip/ServerName;User ID=登陆名;Password=密码 ‘).数据库.dbo.表名
select * from 本地表
SQL Server基本函数
SQL Server基本函数
1.字符串函数 长度与分析用
1,datalength(Char_expr) 返回字符串包含字符数,但不包含后面的空格
2,substring(expression,start,length) 取子串,字符串的下标是从“1”,start为起始位置,length为字符串长度,实际应用中以len(expression)取得其长度
3,right(char_expr,int_expr) 返回字符串右边第int_expr个字符,还用left于之相反
4,isnull( check_expression , replacement_value )如果check_expression為空,則返回replacement_value的值,不為空,就返回check_expression字符操作类
5,Sp_addtype 自定義數據類型
例如:EXEC sp_addtype birthday, datetime, ‘NULL’
6,set nocount {on|off}使返回的结果中不包含有关受 Transact-SQL 语句影响的行数的信息。如果存储过程中包含的一些语句并不返回许多实际的数据,则该设置由于大量减少了网络流量,因此可显著提高性能。SET NOCOUNT 设置是在执行或运行时设置,而不是在分析时设置。SET NOCOUNT 为 ON 时,不返回计数(表示受 Transact-SQL 语句影响的行数)。
SET NOCOUNT 为 OFF 时,返回计数常识 在SQL查询中:from后最多可以跟多少张表或视图:256在SQL语句中出现 Order by,查询时,先排序,后取在SQL中,一个字段的最大容量是8000,而对于nvarchar(4000),由于nvarchar是Unicode码。
SQLServer2000同步复制技术实现步骤一、 预备工作
1.发布服务器,订阅服务器都创建一个同名的windows用户,并设置相同的密码,做为发布快照文件夹的有效访问用户–管理工具–计算机管理–用户和组–右键用户–新建用户–建立一个隶属于administrator组的登陆windows的用户(SynUser)
2.在发布服务器上,新建一个共享目录,做为发布的快照文件的存放目录,操作:我的电脑–D:\ 新建一个目录,名为: PUB–右键这个新建的目录–属性–共享–选择”共享该文件夹”–通过”权限”按纽来设置具体的用户权限,保证第一步中创建的用户(SynUser) 具有对该文件夹的所有权限 –确定
3.设置SQL代理(SQLSERVERAGENT)服务的启动用户(发布/订阅服务器均做此设置)开始–程序–管理工具–服务–右键SQLSERVERAGENT–属性–登陆–选择”此账户”–输入或者选择第一步中创建的windows登录用户名(SynUser)–“密码”中输入该用户的密码
4.设置SQL Server身份验证模式,解决连接时的权限问题(发布/订阅服务器均做此设置)企业管理器–右键SQL实例–属性–安全性–身份验证–选择”SQL Server 和 Windows”–确定
5.在发布服务器和订阅服务器上互相注册企业管理器–右键SQL Server组–新建SQL Server注册…–下一步–可用的服务器中,输入你要注册的远程服务器名 –添加–下一步–连接使用,选择第二个”SQL Server身份验证”–下一步–输入用户名和密码(SynUser)–下一步–选择SQL Server组,也可以创建一个新组–下一步–完成
6.对于只能用IP,不能用计算机名的,为其注册服务器别名(此步在实施中没用到) (在连接端配置,比如,在订阅服务器上配置的话,服务器名称中输入的是发布服务器的IP)开始–程序–Microsoft SQL Server–客户端网络实用工具–别名–添加–网络库选择”tcp/ip”–服务器别名输入SQL服务器名–连接参数–服务器名称中输入SQL服务器ip地址–如果你修改了SQL的端口,取消选择”动态决定端口”,并输入对应的端口号二、 正式配置1、配置发布服务器打开企业管理器,在发布服务器(B、C、D)上执行以下步骤:(1) 从[工具]下拉菜单的[复制]子菜单中选择[配置发布、订阅服务器和分发]出现配置发布和分发向导 (2) [下一步] 选择分发服务器 可以选择把发布服务器自己作为分发服务器或者其他sql的服务器(选择自己)(3) [下一步] 设置快照文件夹采用默认\\servername\Pub(4) [下一步] 自定义配置 可以选择:是,让我设置分发数据库属性启用发布服务器或设置发布设置否,使用下列默认设置(推荐)(5) [下一步] 设置分发数据库名称和位置 采用默认值(6) [下一步] 启用发布服务器 选择作为发布的服务器(7) [下一步] 选择需要发布的数据库和发布类型(8) [下一步] 选择注册订阅服务器(9) [下一步] 完成配置2、创建出版物发布服务器B、C、D上(1)从[工具]菜单的[复制]子菜单中选择[创建和管理发布]命令(2)选择要创建出版物的数据库,然后单击[创建发布](3)在[创建发布向导]的提示对话框中单击[下一步]系统就会弹出一个对话框。对话框上的内容是复制的三个类型。我们现在选第一个也就是默认的快照发布(其他两个大家可以去看看帮助)(4)单击[下一步]系统要求指定可以订阅该发布的数据库服务器类型,SQLSERVER允许在不同的数据库如 orACLE或ACCESS之间进行数据复制。但是在这里我们选择运行”SQL SERVER 2000″的数据库服务器(5)单击[下一步]系统就弹出一个定义文章的对话框也就是选择要出版的表注意: 如果前面选择了事务发布 则再这一步中只能选择带有主键的表(6)选择发布名称和描述(7)自定义发布属性 向导提供的选择:是 我将自定义数据筛选,启用匿名订阅和或其他自定义属性否 根据指定方式创建发布 (建议采用自定义的方式)(8)[下一步] 选择筛选发布的方式 (9)[下一步] 可以选择是否允许匿名订阅1)如果选择署名订阅,则需要在发布服务器上添加订阅服务器方法: [工具]->[复制]->[配置发布、订阅服务器和分发的属性]->[订阅服务器] 中添加否则在订阅服务器上请求订阅时会出现的提示:改发布不允许匿名订阅如果仍然需要匿名订阅则用以下解决办法 [企业管理器]->[复制]->[发布内容]->[属性]->[订阅选项] 选择允许匿名请求订阅2)如果选择匿名订阅,则配置订阅服务器时不会出现以上提示(10)[下一步] 设置快照 代理程序调度(11)[下一步] 完成配置当完成出版物的创建后创建出版物的数据库也就变成了一个共享数据库有数据 srv1.库名..author有字段:id,name,phone, srv2.库名..author有字段:id,name,telphone,adress 要求: srv1.库名..author增加记录则srv1.库名..author记录增加 srv1.库名..author的phone字段更新,则srv1.库名..author对应字段telphone更新 –*/ –大致的处理步骤 –1.在 srv1 上创建连接服务器,以便在 srv1 中操作 srv2,实现同步 exec sp_addlinkedserver ‘srv2′,”,’SQLOLEDB’,’srv2的sql实例名或ip’ exec sp_addlinkedsrvlogin ‘srv2′,’false’,null,’用户名’,’密码’ go–2.在 srv1 和 srv2 这两台电脑中,启动 msdtc(分布式事务处理服务),并且设置为自动启动。我的电脑–控制面板–管理工具–服务–右键 Distributed Transaction Coordinator–属性–启动–并将启动类型设置为自动启动 go –然后创建一个作业定时调用上面的同步处理存储过程就行了 企业管理器 –管理 –SQL Server代理 –右键作业 –新建作业 –“常规”项中输入作业名称 –“步骤”项 –新建 –“步骤名”中输入步骤名 –“类型”中选择”Transact-SQL 脚本(TSQL)” –“数据库”选择执行命令的数据库 –“命令”中输入要执行的语句: exec p_process –确定 –“调度”项 –新建调度 –“名称”中输入调度名称 –“调度类型”中选择你的作业执行安排 –如果选择”反复出现” –点”更改”来设置你的时间安排 然后将SQL Agent服务启动,并设置为自动启动,否则你的作业不会被执行 设置方法: 我的电脑–控制面板–管理工具–服务–右键 SQLSERVERAGENT–属性–启动类型–选择”自动启动”–确定. –3.实现同步处理的方法2,定时同步 –在srv1中创建如下的同步处理存储过程 create proc p_process as –更新修改过的数据 update b set name=i.name,telphone=i.telphone from srv2.库名.dbo.author b,author i where b.id=i.id and(b.name i.name or b.telphone i.telphone) –插入新增的数据 insert srv2.库名.dbo.author(id,name,telphone) select id,name,telphone from author i where not exists( select * from srv2.库名.dbo.author where id=i.id) –删除已经删除的数据(如果需要的话) delete b from srv2.库名.dbo.author b where not exists( select * from author where id=b.id)go
13 2月
AIRKinect 1.7.1 Release
Current Release version: 1.7.1
Whats New in 1.7.1?
- Bug Fixes to Spacial Mapping
AIRKinect 1.7.1 ANEs, SWCs, and DOCs can be found here.
https://github.com/AS3NUI/airkinect-1-release
AIRKinect Extended Library and docs are located here also
https://github.com/AS3NUI/airkinect-1-release
Here are the links to our Open Source Repos
AIRKinect 1.7.1 core
AIRKinect 1.7.1 Core Exmaples
AIRKinect 1.0.1 Extended
AIRKinect 1.0.1 Extended Exmaples
Lastly the Windows Installer binaries have been updated with the latest ANE so you can simply download those and check them out here at out AIREkinect Release Download Page
9 2月
后期处理单元之四 包围曝光HDR合成 全篇结束
我们在前面已经讲过:曝光包围+HDR合成等于把相机宽容度向亮端和暗端延伸。曝光包围增或减的EV向外扩展多少(例如1个EV),就是把宽容度往两端各延伸多少,因此曝光包围是一个非常有用和有效的功能。
但是曝光包围必须有HDR合成的支持才能发挥最大作用,否则和单片摄影并没有什么本质区别,只不过多了一个比较选择单片的机会而已。
许多新摄友之所以放弃使用曝光包围,其中一个重要原因是不会后期合成。因此我着重介绍HDR合成软件和有关操作。
下面是我在夕阳下照的一组曝光包围相片,延伸幅度夸张一点,用了正负1个EV。摄影对象为一个白瓷花瓶。以单张照片而论,有的高光过曝,有的暗部欠曝。图像如下:
1

相机品牌:Canon 相机型号:Canon EOS 550D 镜头:EF-S15-85mm f/3.5-5.6 IS USM
曝光:光圈优先 光圈:F5.7 ISO:100 曝光补偿:0 EV 曝光时间:1/400 sec
图1
2

相机品牌:Canon 相机型号:Canon EOS 550D 镜头:EF-S15-85mm f/3.5-5.6 IS USM
曝光:光圈优先 光圈:F5.7 ISO:100 曝光补偿:-1 EV 曝光时间:1/800 sec
图2
3

相机品牌:Canon 相机型号:Canon EOS 550D 镜头:EF-S15-85mm f/3.5-5.6 IS USM
曝光:光圈优先 光圈:F5.7 ISO:100 曝光补偿:1 EV 曝光时间:1/200 sec
图3
4、合成后的图片宽容度得到改善,暗部和亮部的细节都显示得比较好,画质优于单张相片。
如下图

相机品牌:Canon 相机型号:Canon EOS 550D
曝光:光圈优先 光圈:F5.6 ISO:100 曝光补偿:1 EV 曝光时间:1/200 sec
图4
我使用的HDR合成软件是Photoshop。有些软件虽然也能做HDR合成,如光影魔术手,但不能移除重影,所以只适合做上脚架拍摄的曝光包围合成,不适用于手持拍摄。Photoshop(CS5)可以勾选“移去重影”,所以不但可以用于上架摄影,也可以用于手持拍摄,还可以修改一些重要参数,改善画质,所以是一个易学而实用的软件。
我处理上述相片的过程如下:
1、点击“文件”—“自动”—“合成到HDR pro”

2、出现如下菜单。点击“浏览”,输入需要合成的图片(并不限于3张,多于2张均可),
然后点击“确定”

3、出现默认的合成画面

4、如果重合得不好,可以勾选上方的“移去重影”。接着调整各项参数。很重要的一项是“细节”。因为宽容度扩展了以后,对比度相应会降低。调节“细节”有利于提高锐度。我的调整结果如下:

5、点击“确定”,返回Photoshop画面,出现完成调整的合成图像

以后就是常规的图像调整了,最后的成果如上面的图4。
写到这里,我回头纵览了论坛的作品,觉得需要拾遗补缺帮助新入门兄弟掌握的东西,基本就是这些了,因此我打算就此打住,将【学海无涯】的写作暂告一个段落,以后再根据需要补充。
在此结束之际,我要衷心感谢各位的浏览和鼓励,你们的热情支持是使我能坚持写作的力量源泉。余火髦矣,心愿和承诺已了,确实感到有点精疲力竭了,好在我们的管理力量已经不断壮大和充实,因此请各位允许我偷懒一段时间,充当一阵闲人。踹口气,补补神,然后再回来和弟兄们一起交流提高,共享摄影之乐。谢谢了!
![T2ZlSFXlFbXXXXXXXX_!!62058033[1]](https://snowyrock.files.wordpress.com/2013/02/t2zlsfxlfbxxxxxxxx_620580331.jpg?w=570&h=570)